Nutrition facts labels can seem confusing, but having the ability to read them allows individuals to make informed and healthy nutrition choices. This post breaks down the different components of nutrition labels and provides tips on how to choose the most nutritious foods. It also reviews common food label claims and discusses what they really mean.
Understanding the basics of Nutrition Facts Labels
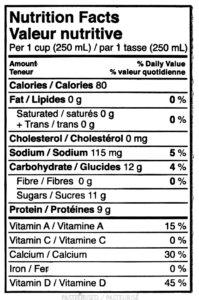
The major components to understand on a nutrition facts label are serving size, servings per container, calories, and % daily value. The FDA sets guidelines that determines the serving size amount on food labels. These include common household measures, reference amounts based on food consumptions surveys, practicality, and clarity. This amount is meant to reflect typical consumption patterns, but it doesn’t necessarily reflect how much you should eat. The information listed on the nutrition label reflects the amount of macro and micronutrients that are in one serving size. The servings per container indicates how many individual servings are in the food package. This can be useful for calculating the nutrition facts of an entire container of food.
The calories reflect the total amount of energy in one serving size. This value is important if you are tracking your calories to lose or gain weight. It can also be helpful when trying to make nutritious choices, if a product is calorically dense it may be high in added sugar or fat and might be best to avoid or enjoy in moderation. The % daily value is the percentage of the recommended daily intake for a specific nutrient that one serving of the product provides. The % daily value is based on a 2,000 calorie per day diet and recommended daily values set by the FDA. If a % daily value is 5% or less, it’s considered to be low in that nutrient. If a % daily value is 20% or more, it’s considered to be high, providing a significant amount of that nutrient for the day. Understanding the % daily value can help people make food choices based on nutrient content, such as if the food is high in fat or sugar, or low in fiber or protein.
 Macronutrients
Macronutrients
There are 3 macronutrients: fat, protein, and carbohydrates. The body breaks down macronutrients to create energy. There are different types of fats, including unsaturated fat, saturated fat, and trans fats. Unsaturated fats are considered healthy fats and help to promote good heart health. Saturated fats and trans fats are considered unhealthy and contribute to an increased risk of heart disease.
A nutrition facts label will list the saturated and trans fat content, which is helpful for identifying what foods are high in unhealthy fats. It’s recommended to limit saturated fats to 10% of your daily calories and to limit trans fat to less than 1% of your daily calories. Cholesterol content is another requirement for a food label. Cholesterol is a type of lipid and is a waxy, fat-like substance found mainly in animal products. It’s needed for bodily functions, but only in limited amounts, especially for individuals with heart disease.
Protein is a macronutrient that is a key factor in muscle growth and repair. Daily protein recommendations are different for each individual based on their height, weight, health condition, and other factors. This value is helpful to understand if you are trying to maintain a high protein diet and are picking out packaged items such as granola bars and cereal.
Nutrition labels have certain guidelines for listing the carbohydrate content of an item. Total carbohydrates must be shown, as well as dietary fiber, sugar, and added sugar. From these values, an individual could also find out how many starches are in the food as well, even though they are not listed. You would do so by subtracting the sum of the dietary fiber and sugar from the total carbohydrates. This is important for individuals who are managing diseases, such as diabetes. This way they can avoid added sugars and identify foods high in fiber.
Micronutrients
Micronutrients are vitamins and minerals that are essential for bodily function. Sodium, potassium, iron, calcium, and vitamin D are the only micronutrients required to be listed by FDA guidelines. Although sodium is technically a micronutrient, it’s listed along with the other macronutrients because of its significant impact on overall health.
Ingredient list
Once you’ve made your way through the macro and micronutrients, you’ll find the ingredients listed towards the bottom. Ingredients are listed in order of quantity, starting with the highest quantity and ending with the lowest. In other words, the first ingredient listed is the largest percentage of the food product. This is important for a number of reasons, one of them is determining if a product is made with mostly whole grains. If a food product is made mostly with whole grains, it will typically be listed as the first or second ingredient.
The ingredients list is also a great place to check for any added sugars, however it might not be listed in these exact words on a label. “Added sugar” may also be called high fructose corn syrup, sucrose, honey, agave nectar, and fructose. These are just a few examples of ingredients that indicate that there has been sugar added to the food product. The ingredient list is also useful for discovering any allergens. If a product contains one of the 9 major allergens, milk, eggs, fish, crustacean shellfish, tree nuts, peanuts, wheat, soybeans, and/or sesame, it must be displayed on the nutrition facts label.
 Special Claims and Food Label Terms
Special Claims and Food Label Terms
Food companies use specific claims and label terms to help sell their products, these claims can be helpful for identifying nutritious foods. Here are a few commonly used claims and what they mean.
- Calorie free: less than 5 calories
- Low calories: 40 calories or less
- Sugar free: less than 0.5 g of sugar
- No added sugar: no sugar or ingredient that contains sugar was added
- Fat free: less than 0.5 g of fat
- Low fat: 3 g of fat or less
- Cholesterol free: less than 2 mg of cholesterol
- Low cholesterol: 20 mg or less of cholesterol
- Sodium free: less than 5 mg of sodium
- Very low sodium: 35 mg of less of sodium
- Low sodium 140 mg or less of sodium
These can be great to look for when managing chronic diseases. For example, individuals with diabetes can look for sugar free or no sugar added food products. Or people with high blood pressure can look for products that say sodium free, very low sodium, or low sodium.
Want to learn more about Nutrition Facts Labels?
Being able to read a nutrition facts label is a powerful tool. It can help with disease management, weight loss, portion control, carb counting, and so much more. It gives you the power to make informed decisions that are going to benefit your overall health. It’s important to remember that everyone is different and a calorie or macronutrient intake that works for one individual may not work for another. There are many different factors that contribute to each person’s nutritional needs. If you’d like to learn more about nutrition facts labels and finding a diet that works for you, schedule a consultation today!
Jalpa is a registered dietitian and nutritionist with a Master’s degree in Health & Nutrition from Brooklyn College, CUNY in New York. She also holds a Certificate of Training in Adult Weight Management through the Academy of Nutrition & Dietetics, CDR.
Related Articles:


