What are the Benefits of a Plant Based Diet?
It seems like more and more people are giving plant based diets a try, and with all of the potential health benefits, there’s no wonder why. They can be more nutrient dense, improve heart health and digestion, lower risk of chronic disease, and more. A plant based diet is even beneficial to the environment. Keep reading to see why a plant based diet may be right for you!
Nutrient Density

Nutrient density refers to the amount of nutrients in foods, relative to how many calories it has. If a food is nutrient dense it means that it holds lots of nutrients, but is low in calories. Some of the most nutrient dense foods are fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, all plant based products. Animal products contain an abundance of nutrients, but are typically higher in calories and fat. This means that you’d have to consume more calories to obtain the same amount of nutrients that you would receive from plant based products.
Nutrient dense food items are high in fiber, vitamins and minerals, and antioxidants. All of these nutrients have different roles that are beneficial to our overall health. Fiber is great for digestion and helps us to feel full throughout the day, it also helps to stabilize blood sugar levels. Vitamins and minerals play many different roles throughout our body, from eye health to fighting infection. Antioxidants help to fight inflammation and oxidative stress which is beneficial for disease management and prevention.
Key Health Benefits of a Plant Based Diet
A plant based diet has been shown to have various health benefits. One of them being improved cardiovascular health. Because fruits, vegetables, and legumes are high in fiber, rich in vitamins and minerals, and low in saturated fat and sodium, they are great for heart function. Replacing animal products with plant based products can lower blood pressure, cholesterol, and risk of heart disease. As a result, the body is able to circulate blood better and reduce inflammation.
Opting for a plant based diet can also be great for weight management and obesity prevention. Plant based products are typically lower in calories and fat compared to animal products. They are also rich in fiber, which helps to promote fullness and satiety. As a result, individuals may eat less calories on a plant based diet than they would on an animal based diet. Research supports this idea and has shown that a plant based diet is associated with a lower BMI. A healthy BMI is beneficial for overall health and decreases the risk of chronic diseases.
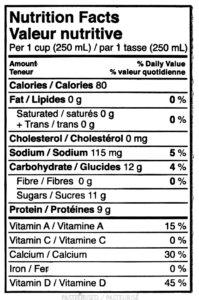
One chronic disease that a plant based diet can manage or prevent is diabetes. Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve insulin sensitivity and stabilize blood sugar levels. This is largely due to the high amount of fiber found in plant based products. Fiber slows down digestion and absorption of carbohydrates into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar and regulating glucose levels. This is key for the prevention and management of all types of diabetes.
The high amounts of fiber found in plant based products is also great for digestion. Fiber helps to bulk stool and promote regular bowel movements, which is beneficial to overall gut health. Having good gut health can prevent bloating, constipation, and certain conditions such as diverticulitis. A diverse plant based diet also provides a variety of vitamins and minerals which supports a diverse and healthy gut microbiome.
Preventing and Managing Chronic Diseases

Along with its many overall health benefits, a plant based diet also has the power to manage and prevent certain chronic diseases, such as cancer, arthritis, and some autoimmune diseases. For example, tomatoes are rich in lycopene which has the power to decrease the risk of prostate cancer. Additionally, a lower BMI, which is associated with a plant based diet, can decrease cancer and chronic disease risk.
Plant based foods are rich in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats which can help to reduce inflammation. Vitamin C, Vitamin E, polyphenols, and carotenoids are key antioxidants found in plant based foods. They have the abilities to alleviate symptoms of arthritis and certain autoimmune diseases. Foods such as turmeric, ginger, berries, leafy greens, and nuts are some of the most anti-inflammatory foods.
How to Ensure Nutritional Balance on a Plant Based Diet
A diverse plant based diet provides many benefits, but there are certain lacking nutrients that are key for overall health. One of these is Vitamin B12, which is mostly found in animal products. Because of this it’s important for individuals on a plant based diet to either take a vitamin B12 supplement or to consume foods that are fortified with vitamin B12. Certain foods that are typically fortified with this vitamin include breakfast cereals, plant based milks, and nutritional yeast.
Individuals on a plant based diet may also not be receiving enough iron and omega 3 fatty acids in their diet since these nutrients are mostly abundant in animal products. Animal products are rich in heme iron, which is easily absorbed by the body. Plant based products are rich in non heme iron, which isn’t as easily absorbed. To compensate for this, it’s important to eat iron rich plant based foods with vitamin C. When iron and vitamin C are consumed together, iron is better absorbed by the body.
Plant based foods rich in iron include beans, dark leafy greens, nuts and seeds, whole grains, and iron fortified foods. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, cruciferous vegetables, and dark leafy greens. Consuming these foods together can help to increase iron absorption. If someone isn’t able to get enough iron from a plant based diet, they could also consider taking an iron supplement, especially if they struggle with iron deficiency anemia.
Fish and seafood are some of the main sources of omega 3 fatty acids, but there are an abundance of plant based foods rich in these as well. Nuts and seeds, plant oils, and certain fortified foods are rich in omega 3 fatty acids. Including a variety of plant based products, fortified foods, and supplementation when necessary can help to prevent certain vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
Want to Learn More About The Benefits of a Plant Based Diet?
Plant based diets have many potential benefits, but it’s important to have variety in your diet, as each food provides different vitamins and minerals that play different roles in the body. Including fortified foods in your diet and supplementation when necessary can help to prevent any potential vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
One thing to know is that you can still reap the benefits of plant based foods without switching to a complete plant based diet. You can try incorporating meatless Monday’s or only having animal products one day per week. Small changes can make a big difference on your overall health and it’s important to find a balance that works best for you.
For guidance on nutrition and balanced diet/ cancer nutrition, contact to set up a consultation!
Jalpa Sheth Nutrition & Wellness, LLC is a nutrition based private practice serving NY, NJ and coming soon FL. Our board certified registered dietitians can be instrumental in helping you attain optimized nutrition to help achieve your goals around health, fitness, sports, and/or mere weight management.
Related Articles:







 Enjoy the Holidays
Enjoy the Holidays
 Macronutrients
Macronutrients Special Claims and Food Label Terms
Special Claims and Food Label Terms




 Find What Works for You
Find What Works for You
 Cope with Your Emotions without Using Food
Cope with Your Emotions without Using Food





 Fall Vegetables
Fall Vegetables




